User Experience Methods Catalogue
A curation of high-quality and helpful user experience methods
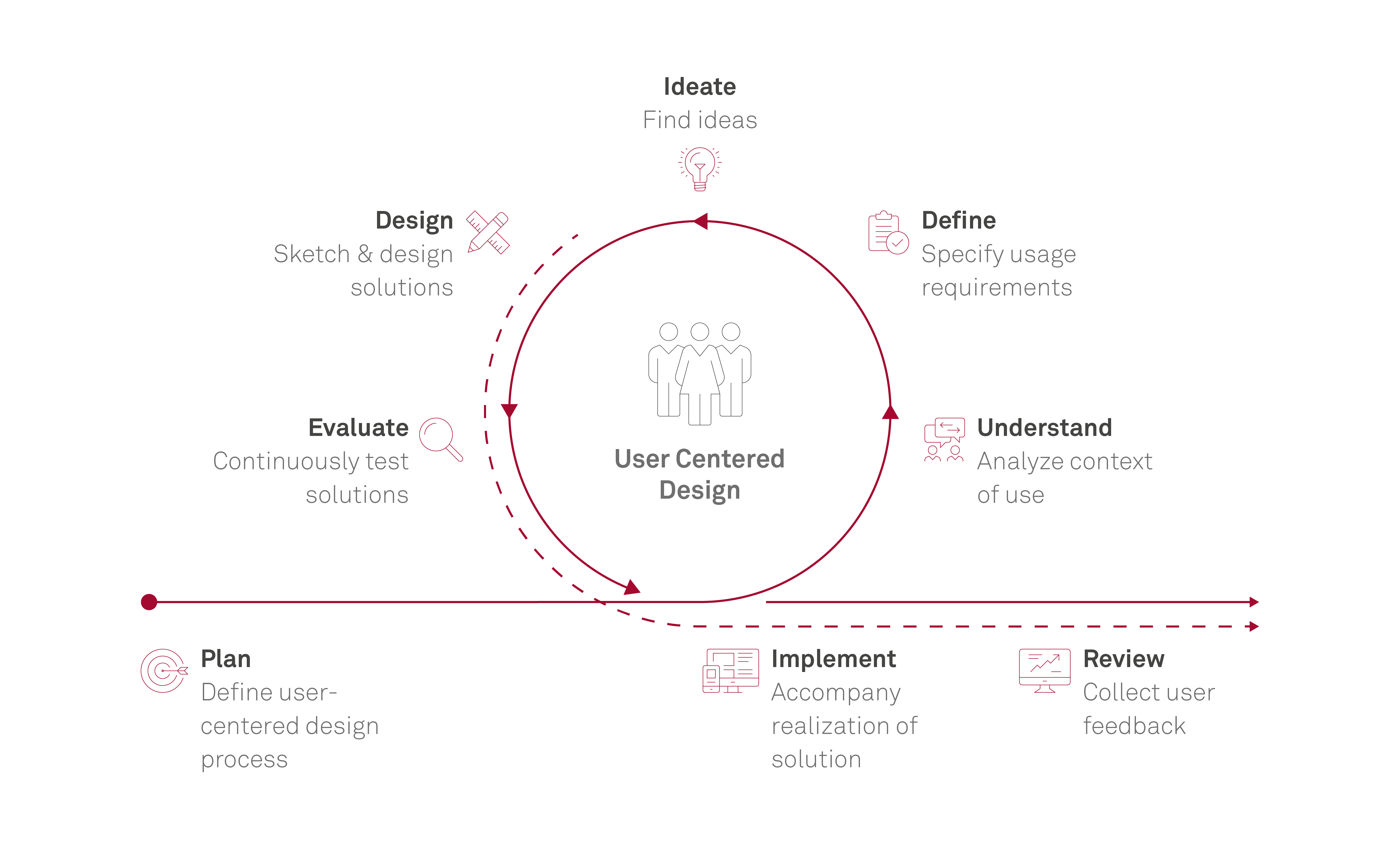
# Understand
- Contextual Inquiry: Contextual inquiries capture the real workflow, ambient conditions and usage context of an application.
- Diary Study: Diary studies record the use of a product in the actual context and over a longer period of time.
- Focus group: Focus groups are moderated group discussions to record experiences and perspectives.
- Observation: Through observation, the real usage context and workflow are recorded.
# Define
- Task model: Description of a user's actions and processes with the interactive system.
- Context of use description: The context of use description summarises the circumstances when an interactive system is used.
- Personas: Personas describe user groups like a profile.
- Storyboard: A comic strip that visualizes the sequence of interaction with the application.
- User Boards: Turning statements and observations from user interviews into structured and meaningful results.
- User Journey Map: User Journey Maps visualize the relationship of a user with a product over time.
- Usage scenario: A usage scenario is a textual description of the interaction with an interactive system.
# Ideate
- 6-3-5 Method: 6 participants, 3 proposals, 5 rounds and plenty of ideas.
- Bodystorming: Experience the context physically and discover new aspects.
- Brainstorming: Quality through quantity: generating new ideas in the group.
- Brainwriting: Brainstorming in silence.
- Dotmocracy: Evaluate and select ideas democratically.
- How-Wow-Now Matrix: How good are our ideas? Evaluation according to feasibility and innovation.
- Yes, and...: Jointly pushing ideas forward.
- Mindmapping: Drawing the mental map on paper.
# Design
- Card Sorting: In card sorting, suggestions for the navigation structure of an application are developed using (paper) cards.
- Cores-and-Paths: Identify and evaluate user goals and operator goals and derive a user-centred structure for the website.
- High fidelity prototype: A high fidelity prototype is already very similar in appearance and interaction to the future interactive application.
- Low fidelity prototype: Low fidelity prototypes take the form of mind maps, sticky notes, and paper sketches.
- Paper prototype: Paper prototypes are a fast and cost-effective way to visualize the basic structure and interactions of an application.
- Styleguide: Styleguides contain concrete specifications for the design of an application.
- Wireframe: A wireframe shows the layout and UI elements of an interactive application.
# Evaluate
- Cognitive Walkthrough: During a cognitive walkthrough, the usability of an interactive system is assessed by experts from the point of view of a user.
- Field Test: In a field test, the interactive application is evaluated in the real context of use.
- Heuristic Evaluation: During a heuristic evaluation the usability of an interactive system is evaluated by experts based on heuristics.
- Laboratory Study / Usability Test: In a usability test the effectiveness, efficiency, and satisfaction of an interactive application is evaluated.
- Questionnaire: Using a (standardized) questionnaire, the usability or user experience of an interactive system can be measured.
- Thinking Aloud: During a usability test, thinking aloud is used to verbalize a subject's thoughts.
- Wizard of Oz prototype: Test functionalities before they exist.